FAST Diagram as Defined in SAVE International®
May 28, 2020 2020-05-28 11:22FAST Diagram as Defined in SAVE International®
FAST Diagram as Defined in SAVE International®
What is FAST Diagram?
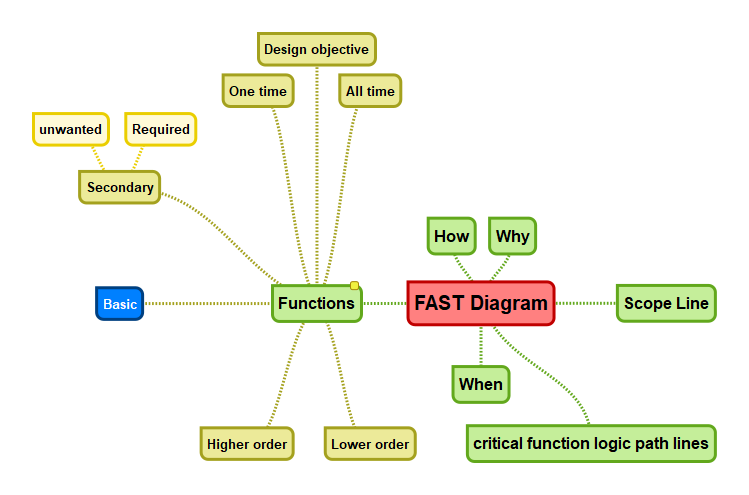
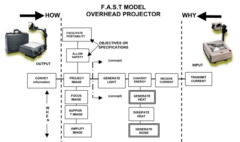
A graphical representation of the dependent relationships of functions within a project, product, or process. The components of a FAST diagram consist of the scope lines; the labeled “How,” “Why,” “When,” and “Subject Scope” arrows; the classified functions, including basic functions, required secondary functions, secondary functions, unwanted secondary functions, higher-order functions, lower-order functions, design objectives, one-time functions, and all-the-time functions; the critical function logic path lines connecting higher-order, basic, required secondary, and lower order functions by their “how” and “why” relationships; and the vertical lines connecting secondary functions to required secondary functions by their “When” relationships.
See why to use Function Analysis System Technique
Function
That which a project, product, or process must do to make it work and meet the customer’s needs. A function identifies “what it does” independent of “what it is,” or “how” it is to be accomplished. It is expressed in a two-word active verb and measurable noun structure. The verb answers the question, “What does it do?” and the noun answers the question, “What does it do it to ?
Function Analysis System Technique (FAST)
Analysis of the dependent relationships of functions within a project, product, or process, which helps to identify and analyze functions to stimulate creativity and innovative thinking. Developed by Charles W. Bytheway.
Function Classifications
The overall categories of functions that are included on FAST diagrams: Basic, Required Secondary, Secondary, Unwanted Secondary, Higher Order, Lower Order, Design Objective, One-Time, and All-the-Time.
Basic Function
The specific purpose(s) for which a project, product, or process exists. It answers the question, “What must it do?”
Secondary Function
A function that supports the basic function or required secondary functions and results from the specific design approach to achieve the basic function.
Required Secondary Function
A function that is necessary in a project, product, or process to perform the basic function. Required secondary functions fall on the Critical Function Logic Path within a FAST diagram.
Unwanted Secondary Function
A negative secondary function caused by the method used to achieve the basic function, e.g., heat generated from lighting, which often must be cooled.
All-the-time Function
A secondary function that happens continuously, anywhere in the performance of the project, product, or process.
One-time Function
A secondary function that occurs only once in the performance of the project, product, or process.
Higher order Function
The specific goal or need for which the basic function exists and is outside the scope of the subject under study.
Lower order Function
The function that is selected to initiate the project, product, or process (an input) and is outside the scope of the subject under study.
Design Objective
Similar and interchangeable with “subject objective” and “project objectives,” these functions express specific compulsory requirements of the project, product, or process.